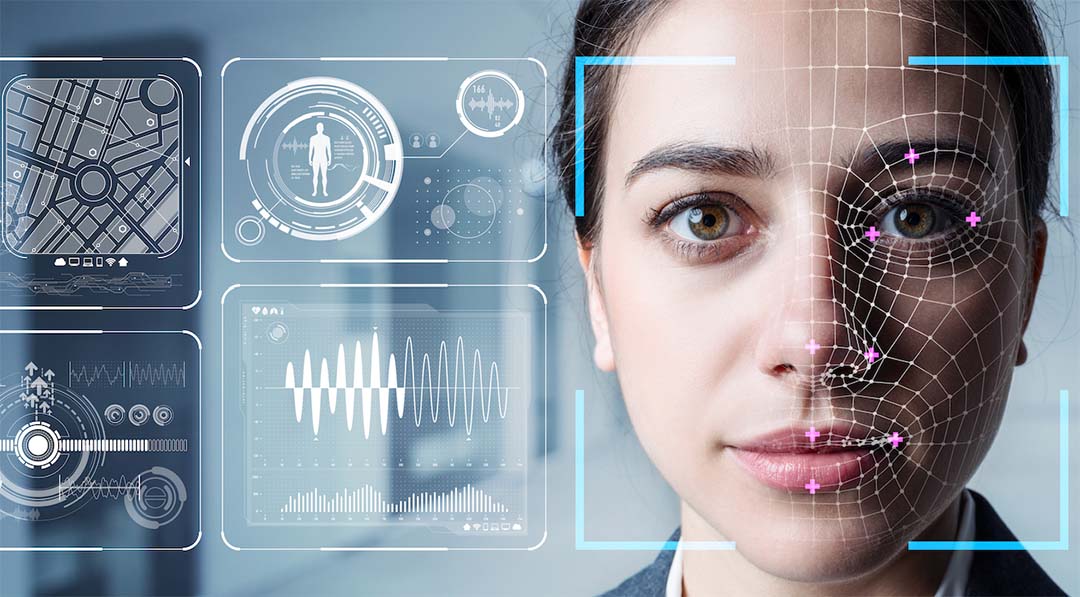
As cyber-attacks continue to rise, cybersecurity experts are meeting the challenge with the innovation of biometric recognition technology. Biometric security utilizes unique human physiological or behavioral characteristics to authenticate and verify the identity of individuals. Unlike traditional methods such as passwords or PINs, which can be forgotten, stolen, or shared, biometric identifiers are inherently personal and difficult to replicate. This makes biometric security an effective means of protecting sensitive information and securing access to devices, systems, and facilities.
Biometric Security Fundamentals
Biometric security harnesses the power of physiological biometrics, behavioral biometrics, or hybrid biometrics.
Physiological Biometrics
Fingerprint Recognition: Fingerprint recognition analyzes the distinctive patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual’s fingertip. Each person’s fingerprints are unique, making this method highly reliable for identity verification.
Iris Recognition: Iris recognition captures the intricate patterns of the iris, the colored part of the eye. Due to the complexity and stability of iris patterns, this method offers a high level of accuracy and is commonly used in high-security environments.
Facial Recognition: Facial recognition systems identify individuals by analyzing facial features such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, and jawline. With the advancements in computer vision technology, facial recognition has become increasingly accurate and widely deployed in various applications.
Behavioral Biometrics
Voice Recognition: Voice recognition analyzes the unique characteristics of an individual’s voice, including pitch, tone, and speech patterns. This method provides a non-intrusive means of authentication and is often used in telephone banking and voice-controlled devices.
Keystroke Dynamics: Keystroke dynamics measure the unique typing patterns of individuals, including typing speed, rhythm, and errors made. By analyzing these behavioral traits, keystroke dynamics can verify the identity of users without the need for additional hardware or sensors.
Hybrid Biometrics
Multimodal Biometrics: Multimodal biometric systems combine multiple biometric modalities, such as fingerprint and facial recognition, to enhance accuracy and reliability. By leveraging complementary biometric traits, multimodal systems provide robust security solutions that are resistant to spoofing and impersonation attacks.
Privacy and Ethical Considerations
Biometric technology is inextricably linked to an individual’s characteristics, bringing privacy and ethical concerns along with it. Sensitive in nature, these uniquely human elements can never be changed, unlike passwords and PINs. Whether a fingerprint, iris, or vocal pattern, safeguarding this data is paramount.
Data Security
Protection of Biometric Data: Biometric data, being highly sensitive and unique to individuals, must be stored and encrypted securely to prevent unauthorized access and potential misuse. Strong encryption algorithms and secure storage mechanisms are essential to safeguard biometric data from cyber threats and data breaches.
Minimization of Data Collection: To mitigate privacy risks and comply with evolving regulations, organizations should limit biometric data collection to only what is necessary for authentication purposes. Collecting excessive or unnecessary biometric data increases the risk of privacy violations and regulatory scrutiny.
Informed Consent
Transparency: Users should be fully informed about how their biometric data will be collected, stored, and used before providing consent. Transparent communication ensures that individuals understand the implications of participating in biometric authentication processes and can make informed decisions about their privacy.
Opt-In Mechanisms: Implementing opt-in mechanisms for biometric authentication allows users to participate voluntarily. By giving users control over their biometric data, organizations demonstrate respect for individual privacy and autonomy.
Developing Trends in Biometric Security
Artificial Intelligence Integration with Machine Learning
Enhanced Accuracy: Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms integrated with machine learning (ML) techniques continually learn from data and adapt to evolving patterns, improving the accuracy and reliability of biometric systems over time. By analyzing vast amounts of biometric data, AI-powered systems can recognize subtle variations and anomalies, leading to more precise identification and authentication.
Real-time Threat Detection: Machine learning algorithms can detect suspicious patterns and anomalies in real-time, enabling proactive threat detection and response. By analyzing biometric data streams in real-time, AI-powered systems can identify unauthorized access attempts or fraudulent activities, enhancing overall security posture.
Mobile Biometric Technology
Convenience: Mobile devices with biometric sensors, such as fingerprint scanners and facial recognition cameras, offer users a convenient and seamless way to authenticate themselves. Instead of entering complex passwords or PINs, users can simply use their biometric traits to unlock their devices and access sensitive information.
Secure Transactions: Mobile biometric technology enables secure authentication for mobile payments and digital transactions. By integrating biometric authentication into mobile banking apps and payment platforms, organizations can enhance the security of financial transactions while providing a frictionless user experience.
Cloud-Based Biometric Solutions
Scalability: Cloud-based biometric solutions offer scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to accommodate growing user bases and fluctuating workloads without significant infrastructure investments. By leveraging cloud resources, organizations can easily scale biometric authentication services to meet the demands of their business operations.
Remote Access: Cloud-based biometric solutions enable secure access to biometric data from anywhere, facilitating remote authentication and identity verification. With the increasing adoption of remote work and mobile devices, cloud-based biometric solutions provide a convenient and secure way to verify identities and grant access to sensitive resources.
Liveness Detection
Preventing Spoofing Attacks: Liveness detection techniques verify that the biometric being presented is from a live person and not a spoof or replication. By analyzing subtle physiological or behavioral cues, such as eye movements or facial expressions, liveness detection algorithms can distinguish between genuine biometric traits and fake replicas, thereby preventing spoofing attacks.
Dynamic Authentication: Incorporating liveness detection into biometric systems enhances security by dynamically adapting authentication processes based on the perceived level of risk. For example, if liveness detection detects suspicious behavior or signs of spoofing, the system can prompt additional authentication measures or deny access until further verification is provided.
Network Security with Cynergy Technology
With over forty-two years of experience, Cynergy Technology is a leading provider of network security solutions. Network security is any activity designed to protect the usability and integrity of your network and data. Our IT professionals leverage various innovative tools and automation to safeguard your IT infrastructure and sensitive data. Biometric security is another state-of-the-art cybersecurity measure Cynergy can implement to give your organization the strongest security posture possible. If you’d like to learn more about Cynergy’s network security services, contact our experts for a free consultation today!